Reference: Essays on Substance
Fields and Particles
According to the AI:
In quantum field theory, a particle being an excitation of a field means that it is a temporary disturbance or oscillation in an underlying quantum field. These quantum fields are continuous and permeate all of spacetime. When a quantum field receives energy, it can create a ripple or excitation that behaves like a particle.
Particles are not individual entities existing on their own, but rather manifestations of these field excitations. For example, an electron is an excitation of the electron field, while a photon is an excitation of the electromagnetic field. These excitations can be thought of as wave packets propagating through their respective fields.
The strength and duration of these excitations determine the nature of the particles:
- Virtual particles: Tiny, fleeting ripples that exist for extremely short periods.
- Real particles: Stronger excitations with definite properties like location and momentum, which can be measured in experiments.
When particles interact or are detected, it involves an exchange of energy between different quantum fields. This exchange can cause the fields to “bunch up” or concentrate at specific locations, which is what we observe as particle behavior.
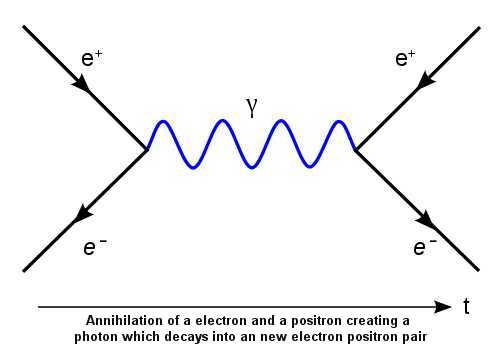
Understanding particles as field excitations helps explain phenomena like particle creation and annihilation, which occur through the interactions and energy exchanges between these fundamental quantum fields.
.
According to Substance Theory:
Spacetime and Field
- Space and time represent dimensions of substance.
- Therefore, any space and time has substance in it.
- A mathematical field could be modeling an actual substance.
Field and particles
- As substance gets concentrated it becomes a particle that is smaller in size and more sluggish.
- A particle exists as a more concentrated substance in a less concentrated background. For example, the electronic region exists within an electromagnetic background.
- This pattern may repeat with the particle becoming the background of a more concentrated particle. For example, the nuclear region exists within the electronic background.
- This pattern may repeat with the background becoming a particle within a still broader and less concentrated background. For example, the electromagnetic region may exist as a particle within aether as its background.
- The particle moves within its background like a “pulse.” It is continuous with its background.
- There is spectrum of particles according to their degree of concentration. This is same as the spectrum of substance.
- There is relative motion among pulses at the same level of concentration.
- As the concentration increases with successive particle-background iterations, the absolute motion decreases.
- With each iteration of “background-particle,” there is creation of mass.
- The least concentrated background may be compared with the mathematical Higgs Field.
- All particles and backgrounds shall be related to each other through the continuity of substance.
- When the backgrounds (fields) interact with each other, the energy generated gets converted into particles.
- Energy is conserved but not the number of particles.
.
